BayMeds v.2103 User Guide
Welcome to the BayMeds User Guide!
This guide provides a step-by-step documentation on how to use BayMeds' features and how to tackle commonly encountered errors. In addition, the quick start guide shows you how to get started in a matter of minutes!
What is BayMeds?
BayMeds v.2103 (a.k.a BayMeds) is your go-to prescription management solution, catering to chronically ill patients or caregivers seeking a streamlined and effective way to track prescriptions. Ideal for those with busy lives and complex medication regimens, BayMeds offer reminders for staying on top of prescription schedules and provides a platform to track prescription consumptions. With a focus on user-friendliness, BayMeds aims to promote medication adherence and reduce misusage.
What can I do with BayMeds?
Track consumption of existing prescriptions
BayMeds filters and shows you your prescriptions to be consumed each day. By marking prescriptions you have consumed, BayMeds will differentiate and show you the prescriptions that are completed and those that have yet to be completed for the day.
Store important details of existing prescriptions
BayMeds allows you to store details crucial to the consumption of the prescription, such as the end and expiry date of the prescription, as well as the current stock of pills available. You may also store specific requirements that a prescription may have, such as restricted consumption to only after heavy meals.
Get warnings for conflicting drugs
BayMeds informs you when you have drugs that conflicts with each other, e.g. drugs that react with other drugs or affect the efficacy of other drugs. This is especially useful for patients with multiple prescriptions, as it helps to prevent the consumption of conflicting drugs.
Track past prescriptions
BayMeds enables storage of past prescriptions, i.e. prescriptions that you have completed in the past. This provides ease of access to such information when required, such as during a Doctor's visit, or when tracking the quantity of medication remaining.
Table of Contents
- How to use this guide
- Quick start
- Graphical User Interface
- Features
- How to add a prescription :
add - How to list all current prescriptions :
list - How to list today's prescriptions :
listToday - How to list completed prescriptions :
listCompleted - How to edit a prescription :
edit - How to find prescriptions by name :
find - How to delete a prescription :
delete - How to take a medication :
take - How to untake a medication :
untake - How to list medications that are about to expire or low in stock :
reminder - How to list a prescription's conflicting drugs :
listConflicts - How to list all conflicting drugs :
listAllConflicts - How to view help :
help - How to exit BayMeds :
exit
- How to add a prescription :
- FAQ
- Known issues
- Command summary
- Troubleshooting
How to use this guide
- Navigate to the start of this guide anytime by clicking the button in the bottom right corner of your screen.
- The blue text in this guide are hyperlinks that will bring you to the relevant section when clicked.
- The
codetext in this guide highlight technical information or commands that you can type into the application.
If you...
- are new to BayMeds, we recommend you to begin at the Quick Start section.
- are an experienced user, you may refer to the Features section to learn more about each command available in BayMeds.
- would like to see all available commands, refer to the Command Summary section.
- are looking to troubleshoot some errors you encountered, you can refer to the Troubleshooting section.
Additionally, here are some common icons you may encounter in this guide.
| Icon | Description |
|---|---|
| Examples | |
| Useful tips | |
| Additional information | |
| Warning |
Quick start
If you are experienced in using JAR applications, simply download the latest version here and start the application.
Starting BayMeds
Ensure you have Java
11or above installed in your computer.Download the latest
BayMeds.jarfrom here.Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for BayMeds.
Open a command terminal,
cdinto the folder you put the jar file in, and use thejava -jar BayMeds.jarcommand to start the application.A GUI similar to the one below should appear in a few seconds. Note how the app contains some sample data.
Adding your first prescription
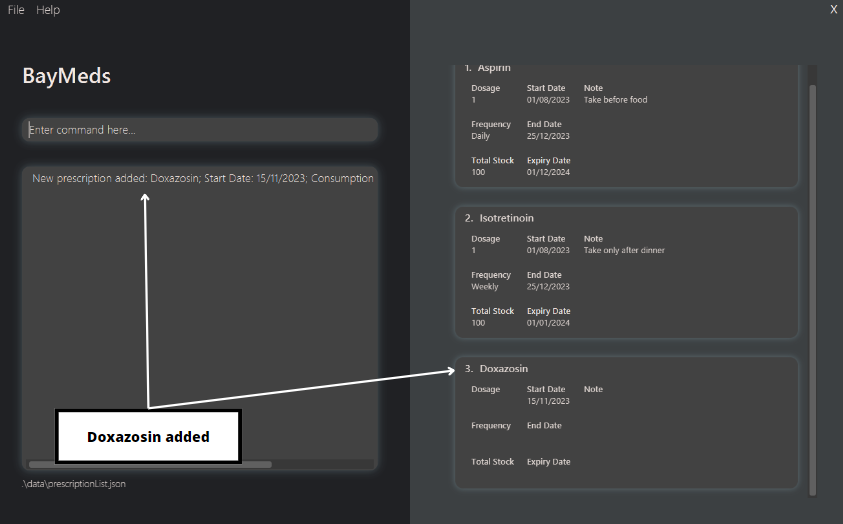
- To add your first prsecription, type
add mn/Doxazosin. You will see your prescription being added into the prescription list, as shown below.
Taking your first prescription
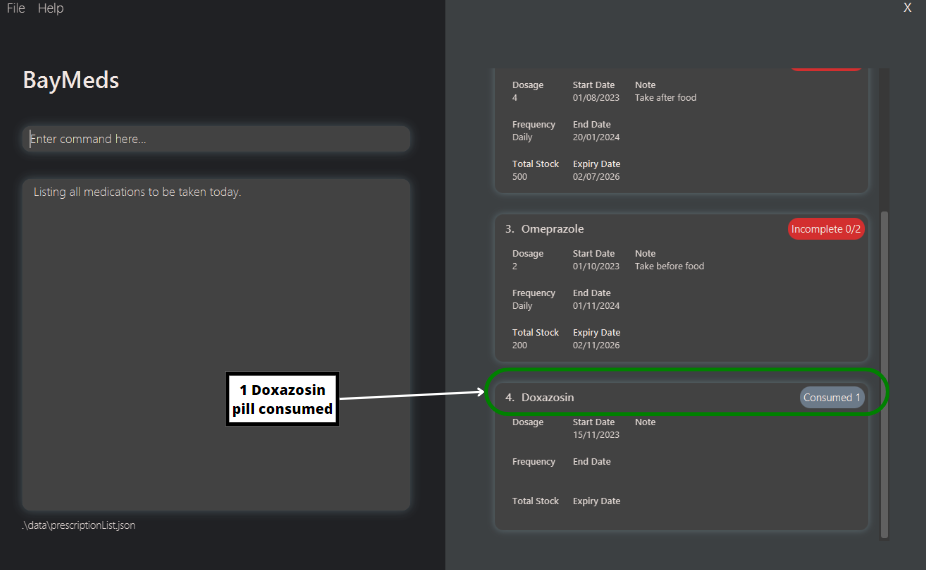
To mark a prescription that you have just consumed, type
take 3 d/1. The third prescription in the list will then be marked as consumed.To check that it has been marked as consumed, you can type
listToday. As seen below, this will show that you have consumed 1 pill of Dosazoxin.
- That is all you have to do to get started! You may wish to refer to the features section below for more details of each command.
Navigating the Graphical User Interface
Overview
BayMeds allows you to manage your prescriptions using only a single user interface! Hover over the circles to find out more about the different components on the screen!

| Number | Component | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Menu Bar | You can access various menu functions here. |
| 2 | Command Box | This is where you will input your commands. |
| 3 | Result Display | BayMeds will show you messages through this box. |
| 4 | List Display | This is where you can view your list of prescriptions. |
Prescription Card
BayMeds organises everything you need to know about your prescriptions in prescription cards, as shown below. Hover over the circles to find out more about each label!
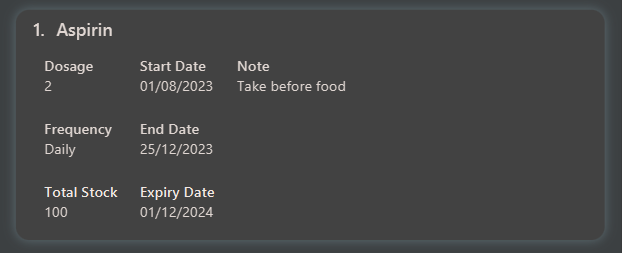
| Number | Component | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Medication Name | This is the name of your medication. |
| 2 | Dosage | This is the number of pills you need to take each day. |
| 3 | Frequency | This is the interval to consume your medication. It can be Daily, Weekly or Monthly. |
| 4 | Total Stock | This is the total number of pills you have. |
| 5 | Start Date | This is the start date of your prescription. |
| 6 | End Date | This is the end date of your prescription. |
| 7 | Expiry Date | This is the expiry date of your medication. |
| 8 | Note | This is where you can see personal notes for your prescription. |
Features
Notes about the command format
Words in
<>are parameters you can enter.Example
For
add mn/<medication_name>,<medication_name>is a parameter which can be used asadd mn/Aspirin.Items in
[]are optional.Example
<medication_name> [sd/<start_date>]can be used asmn/Aspirin sd/25/10/2023or asmn/Aspirin.Parameters can be in any order.
Example
For
mn/<medication_name> f/<frequency>,f/<frequency> mn/<medication_name>is also acceptable.If you are using a PDF version of this document, be careful when copying and pasting commands that span multiple lines as space characters surrounding line-breaks may be omitted when copied over to the application.
How to add a prescription : add
Upon getting a new prescription from the doctor, BayMeds allows you to add the prescription to the list.
To add the prescription, type the following command.
Format:
add
mn/<medication_name>
[d/<dosage>]
[f/<frequency>]
[sd/<start_date>]
[ed/<end_date>]
[exp/<expiry_date>]
[ts/<total_stock>]
[cfdg/<conflicting_drugs>]
[n/<note>]
The prescription will then be added and shown in the list.
Notes
<medication_name>refers to the name of the medication.Example
Aspirin, Doxazosin, Propranolol
<dosage>refers to the number of pills to be taken. It only accepts a numeric value.Example
For 1 pill, type 1.
<frequency>refers to the interval to consume the prescription. It only accepts the inputsDaily,WeeklyorMonthly.<start_date>,<end_date>and<expiry_date>should be in dd/mm/yyyy format. In addition,<expiry_date>cannot be earlier than the<end_date>, and similarly,<end_date>cannot be earlier than the<start_date>.Example
For 20th September 2023, type
20/09/2023.<total_stock>refers to the total number of pills you have. It only accepts a numeric value.Example
For 100 pills, type 100.
<conflicting_drugs>refers to the drugs that conflict with your prescription. You may add in multiple conflicting drugs by separating them with a space.Example
If you wish to add Paracetamol and Aspirin as conflicting drugs to your prescription, type
cfdg/Paracetamol Aspirin.<note>refers to any important or special information you would like to include.Example
"To be taken after meals". "Take after food".
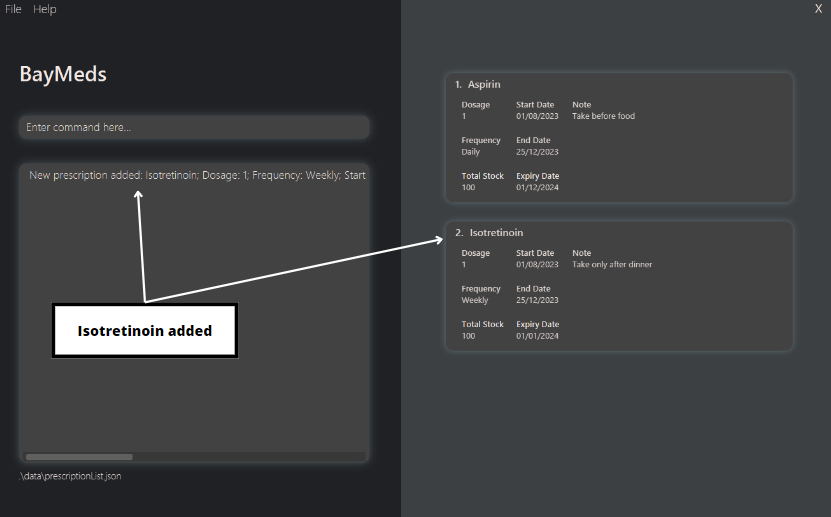
add mn/Isotretinoin d/1 f/Weekly sd/01/08/2023 ed/25/12/2023 exd/01/01/2024 ts/100 n/Take only after dinner
By typing this, you will add a new prescription with the following information.
- Medication name: Isotretinoin
- Dosage: 1
- Frequency: Weekly
- Start date: 01/08/2023
- End date: 25/12/2023
- Expiry date: 01/01/2024
- Total stock: 100
- Note: Take only after dinner
After successfully adding the prescription, you will get the following result:
add mn/Doxazosin
By typing this, you will add a new prescription with the following information.
- Medication name: Doxazosin
After successfully adding the prescription, you will get the following result:
As shown in this example, the date of which this entry was entered (e.g. 27/10/2023) will be used as the default start date if no start date was given.
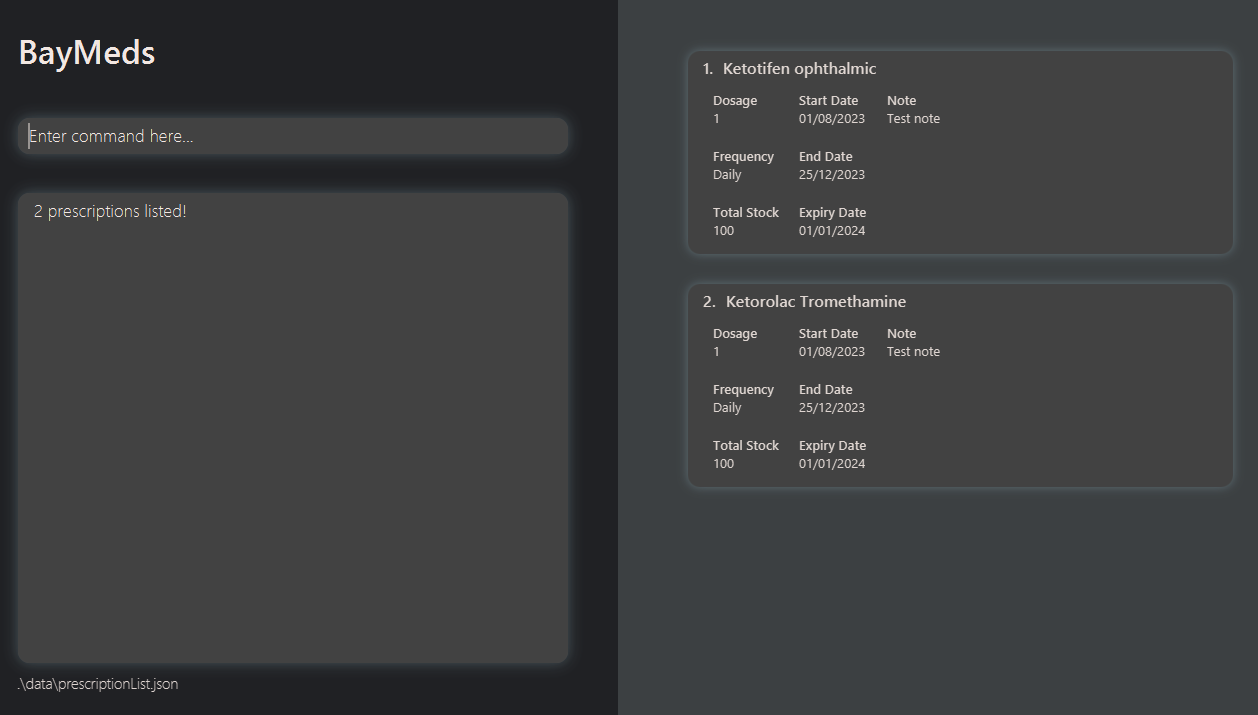
How to list all current prescriptions : list
BayMeds allows you to list all prescriptions you are currently taking.
To list all current prescriptions, type the following command.
Format:
list
You will then be able to see the relevant prescriptions in the list.
Notes
If you would like to only view prescriptions that you have to consume for the day, use listToday instead.
If you would like to view prescriptions that you have consumed in the past, use listCompleted instead.
How to list today's prescriptions : listToday
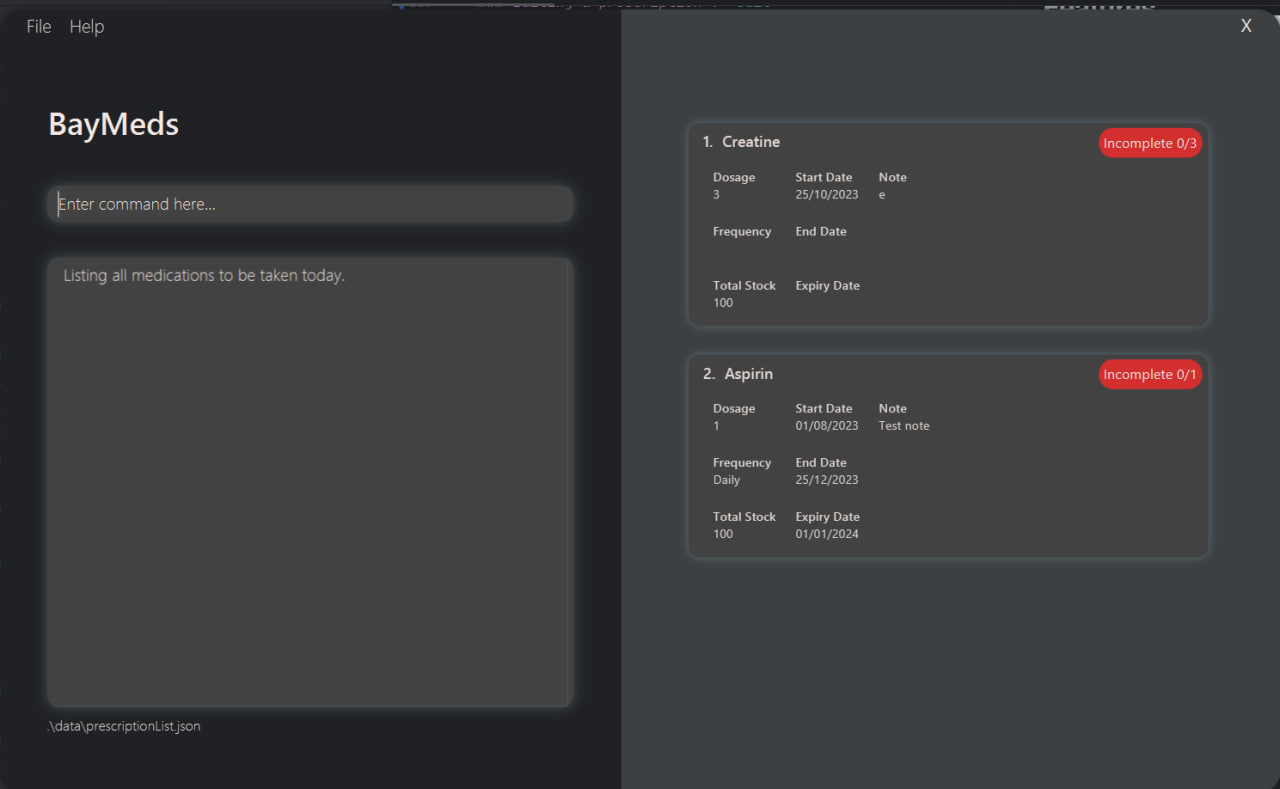
BayMeds allows you to list all prescriptions that you need to consume for the day.
To list these prescriptions, type the following command.
Format:
listToday
You will then be able to see the relevant prescriptions in the list.
Notes
Only the medications to be taken for the day will be displayed.
Medications to be taken are determined by their frequency and start dates.
Example
If the
<frequency>of a particular prescription isDaily, it will appear in this list everyday.If the
<frequency>of a particular prescription isWeekly, and the<start_date>falls on a Wednesday, it will appear in this list only on Wednesdays.In this list, prescriptions will have an indicator, on the top right, to show the number of pills consumed and whether or not it has been completed for the day. In the event that
<dosage>was not provided, the indicator will instead display the amount you have consumed for the day.As
<frequency>is an optional input, prescriptions that do not have a frequency will continue to appear in this list. This is so that in the event you are unaware of the frequency, or if the frequency is irregular, you may continue to track the prescription consumption if you wish to take it on that day.If you would like to view prescriptions that you are currently taking, use list instead.
If you would like to view prescriptions that you have consumed in the past, use listCompleted instead.
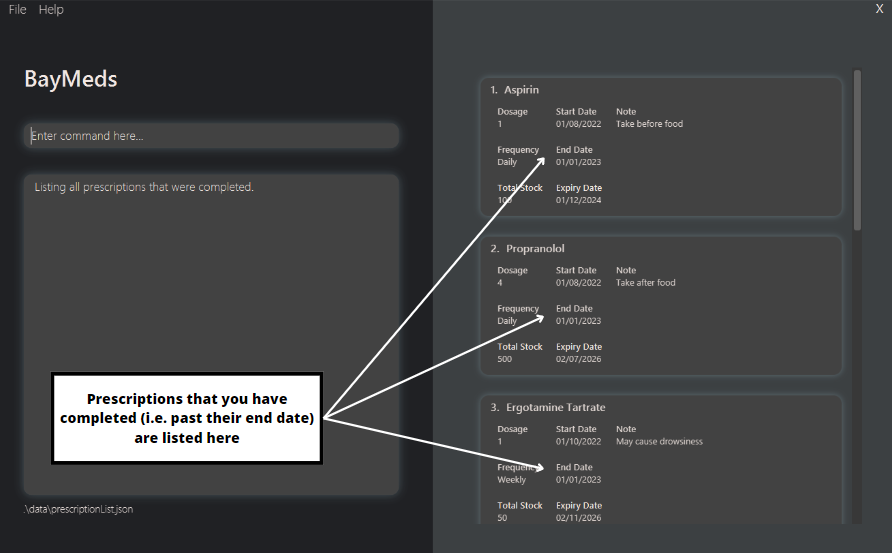
How to list completed prescriptions : listCompleted
BayMeds allows you to list prescriptions that you have consumed in the past.
To list these prescriptions, type the following command.
Format:
listCompleted
You will then be able to see the relevant prescriptions in the list.
Notes
If you would like to view prescriptions that you are currently taking, use list instead.
If you would like to only view prescriptions that you have to consume for the day, use listToday instead.
Important
The list of prescriptions shown after using this command will not respond to other commands such as add, edit, take etc. This is because this list is meant to store your consumption history for record-keeping purposes. Thus, apart from viewing these prescriptions, other interactions with this list are intentionally disabled.
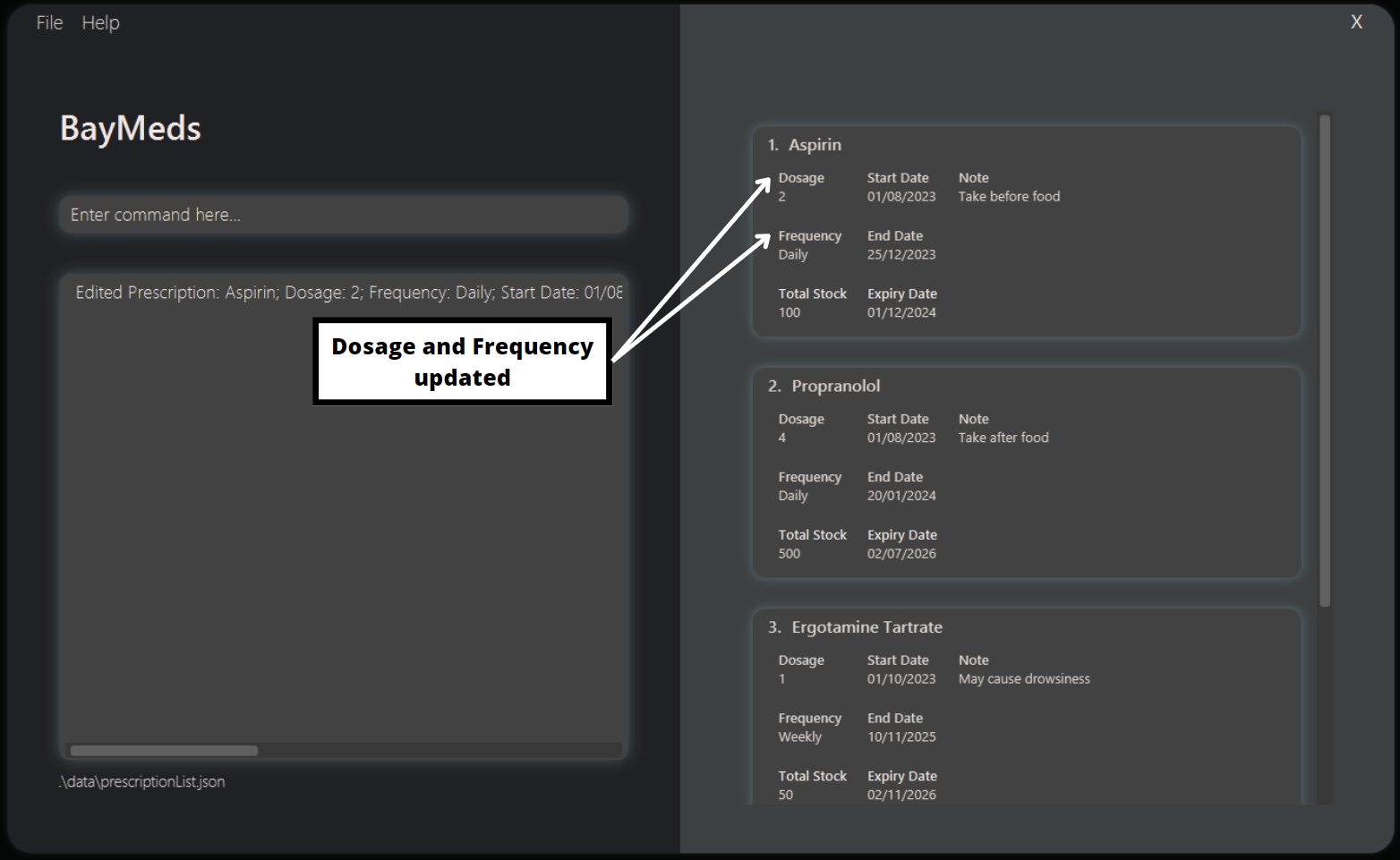
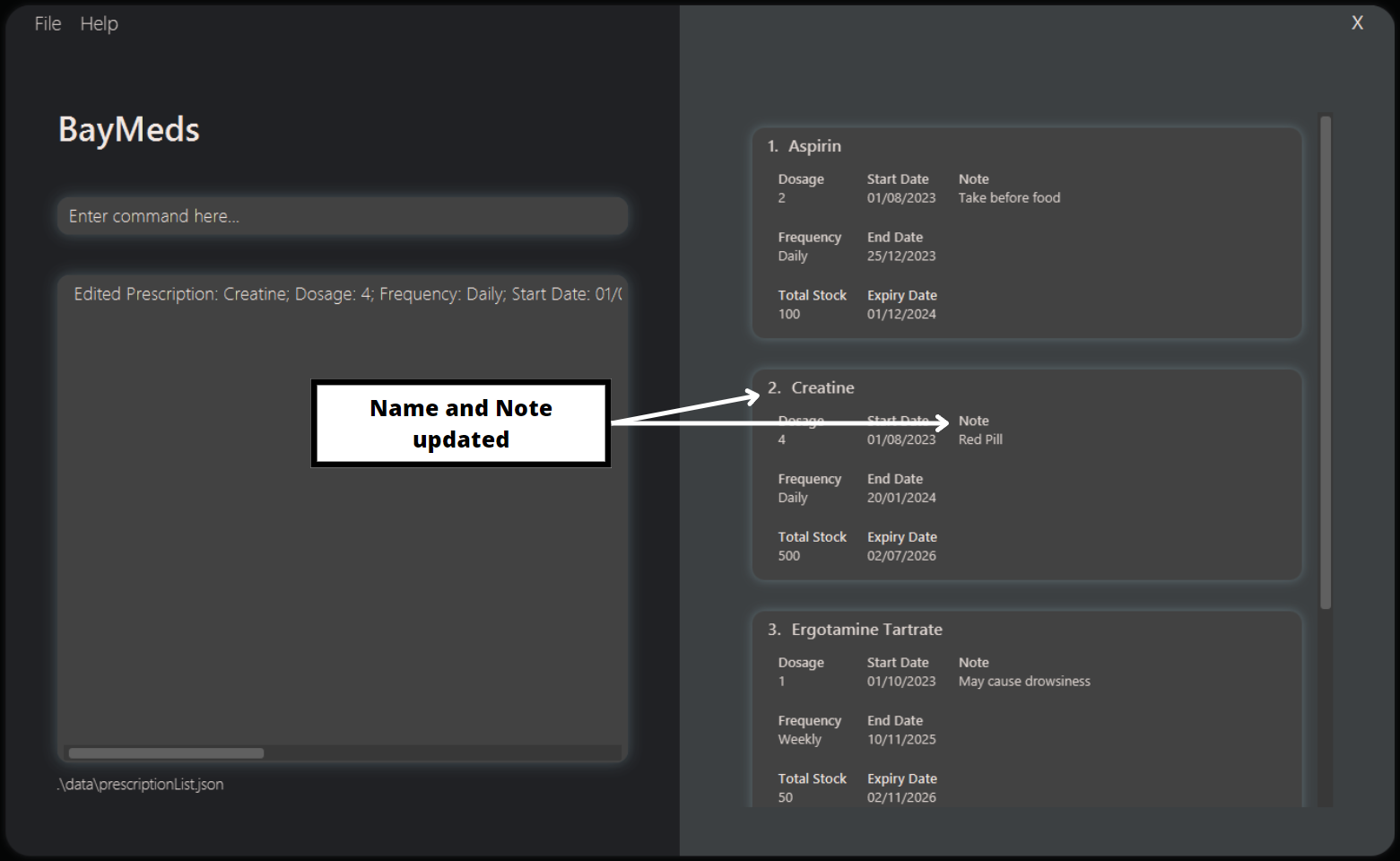
How to edit a prescription : edit
You may wish to update any of the fields of the prescription for a variety of reasons, such as a change in dosage, or an increase in stock. BayMeds allows you to edit such fields in the prescription.
To edit a prescription, type the following command.
Format:
edit
<index>
[mn/<medication_name>]
[d/<dosage>]
[f/<frequency>]
[sd/<start_date>]
[ed/<end_date>]
[exd/<expiry_date>]
[ts/<total_stock>]
[cfdg/<conflicting_drugs>]
[n/<note>]
Based on the fields you specify, the corresponding fields of the index-identified prescription will be updated with the new value. Fields that are not specified will continue to remain the same.
Notes
The
<index>specifies the prescription to be edited.Example
To edit the first prescription in the list (currently being displayed), specify the
<index>as 1.At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
Input values cannot be empty.
How to find prescriptions by name : find
With a complex medication regimen, BayMeds allows you to easily filter and find your prescriptions with names that contain the specified keyword.
To find matching prescriptions, type the following command.
Format:
find <keyword>...
Notes
The
...indicates that you can include multiple<keywords>.Example
You can indicate
find Ketoconazole Shampoo.The search is case-insensitive.
Example
find paracetamolwill also matchParacetamol.The order of the keywords does not matter.
Example
find Ketoconazole Shampoowill matchShampoo Ketoconazole.Only the medication name is searched and matched.
Substrings will be matched.
Example
find Parawill matchParacetamol.Prescriptions will be matched as long as any part of it matches the
<keyword>.Example
Ketorolac ophthalmicwill return bothKetotifen ophthalmicandKetorolac Tromethamine.
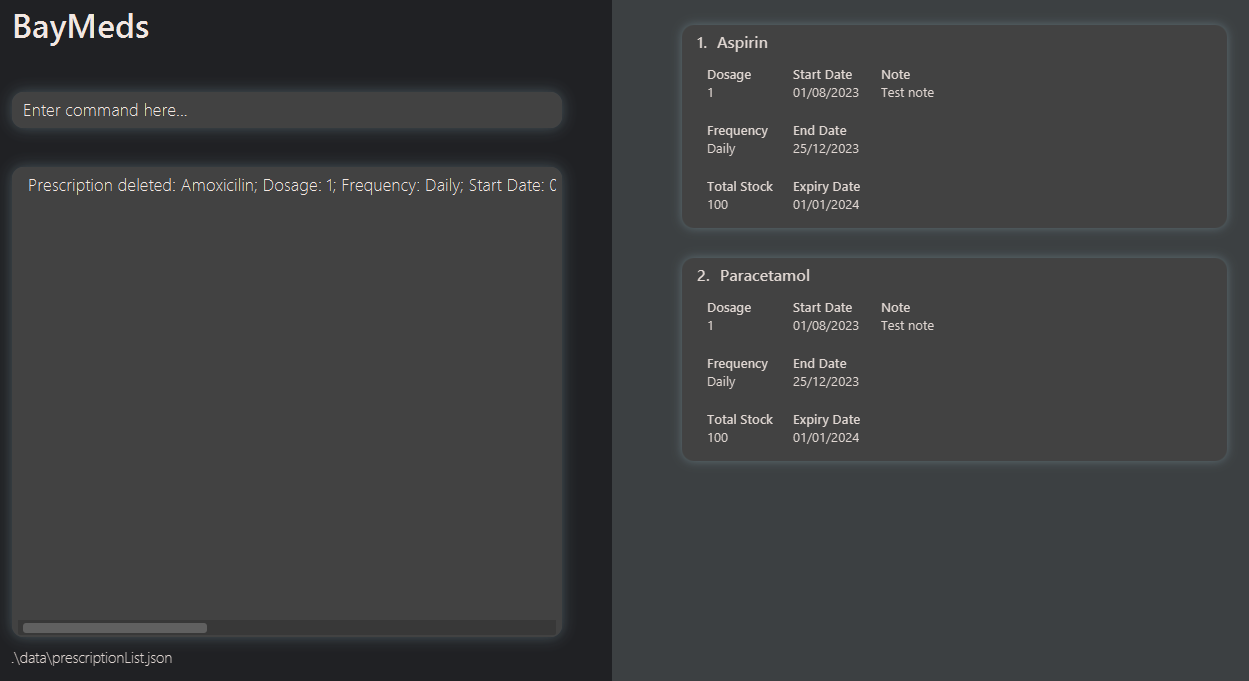
How to delete a prescription : delete
Should you need to remove your prescriptions, BayMeds allows you to permanently delete a specified prescription from the list (currently being displayed).
To delete a prescription, type the following command.
Format:
delete <index>
This will cause the prescription at that index to be removed from the list (currently being displayed) and permanently deleted.
Notes
The
<index>specifies the prescription to be deleted.Example
To delete the first prescription in the list (currently being displayed), specify the
<index>as 1.The prescription that will be removed will be the prescription at the specified index of the currently displayed list (list or listToday). This command will not affect the completed prescription list.
How to take a medication : take
Upon consuming a medication, you may wish to indicate that you have taken 1 / 4 pills, or that you have completed your dosage for the day. BayMeds allows you to update prescriptions with the amount of dosage you have taken.
In order to do so, type the following command.
Format:
take
<index>
[d/<dosage>]
This will update the index-identified prescription with the specified amount of <dosage>.
Notes
The
<index>specifies the prescription to be marked as taken.Example
To update the first prescription in the list (currently being displayed), specify the
<index>as 1.<dosage>refers to the number of pills you have taken. It only accepts a numeric value.Example
If you have taken 2 pills, specify the
<dosage>as 2.Since
<dosage>is an optional input, it will be set as 1 if no input is given.The amount consumed will be increased by the specified
<dosage>.The stock field of the prescription will be decreased by the specified
<dosage>.If you would like to see the updated consumption count and stock, use listToday.
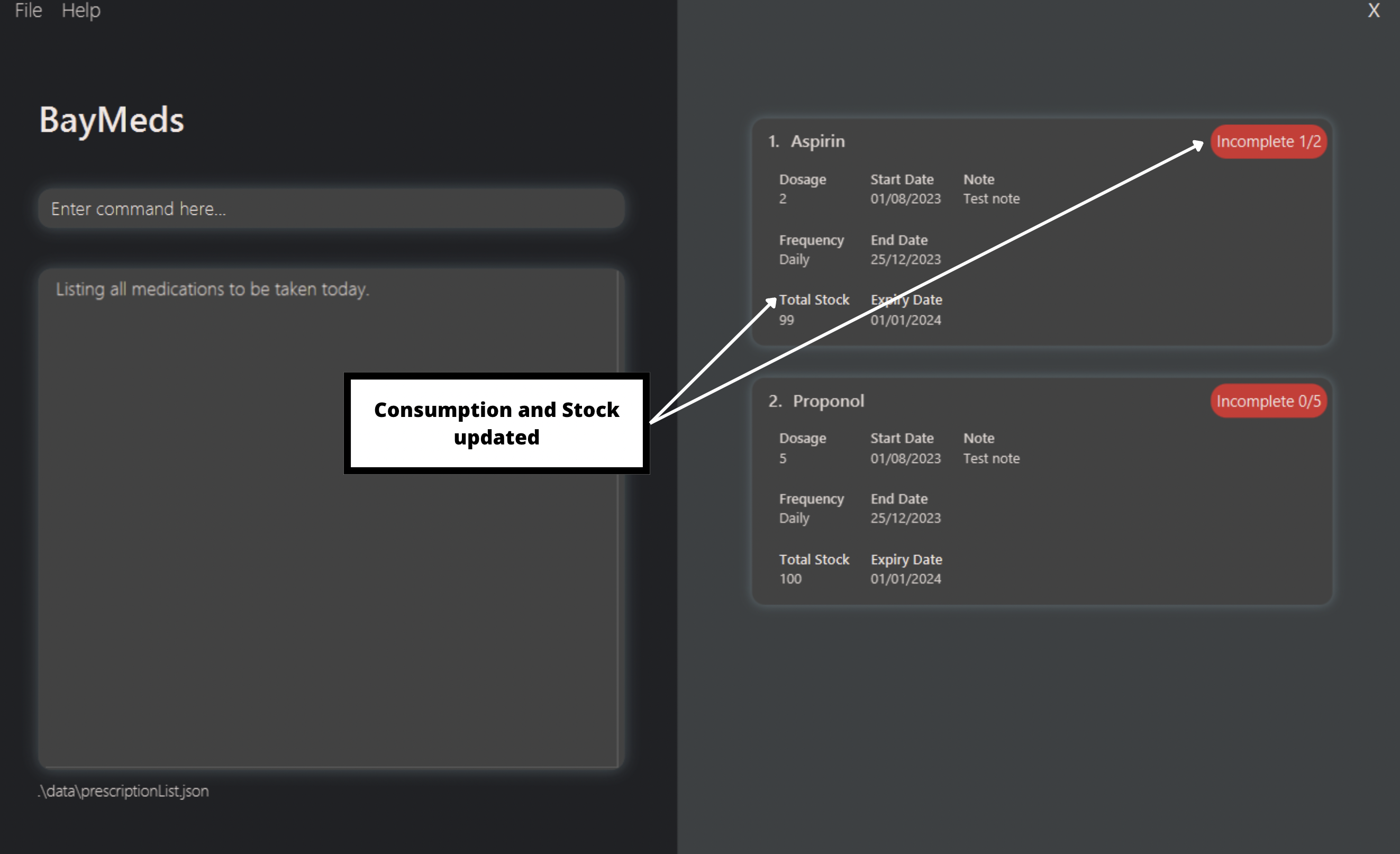
How to untake a medication : untake
If you have accidentally indicated that you have taken a medication, and you wish to undo this, Baymeds allows you untake the medication similar to the take feature.
Note that this feature is meant to revert errors made by the user, updating changes to the stock and consumption count.
In order to do so, type the following command.
Format:
untake
<index>
[d/<dosage>]
This will update the index-identified prescription with the specified amount of <dosage> to be removed.
Notes
The
<index>specifies the prescription to be marked as taken.Example
To update the first prescription in the list (currently being displayed), specify the
<index>as 1.<dosage>refers to the number of pills you want to mark as not consumed. It only accepts a numeric value.Example
If you wish to mark 2 pills of the prescription as not consumed, specify the
<dosage>as 2.Since
<dosage>is an optional input, it will be set as 1 if no input is given.The amount consumed will be decreased by the specified
<dosage>.The stock field of the prescription will be increased by the specified
<dosage>.If you would like to see the updated consumption count and stock, use listToday.
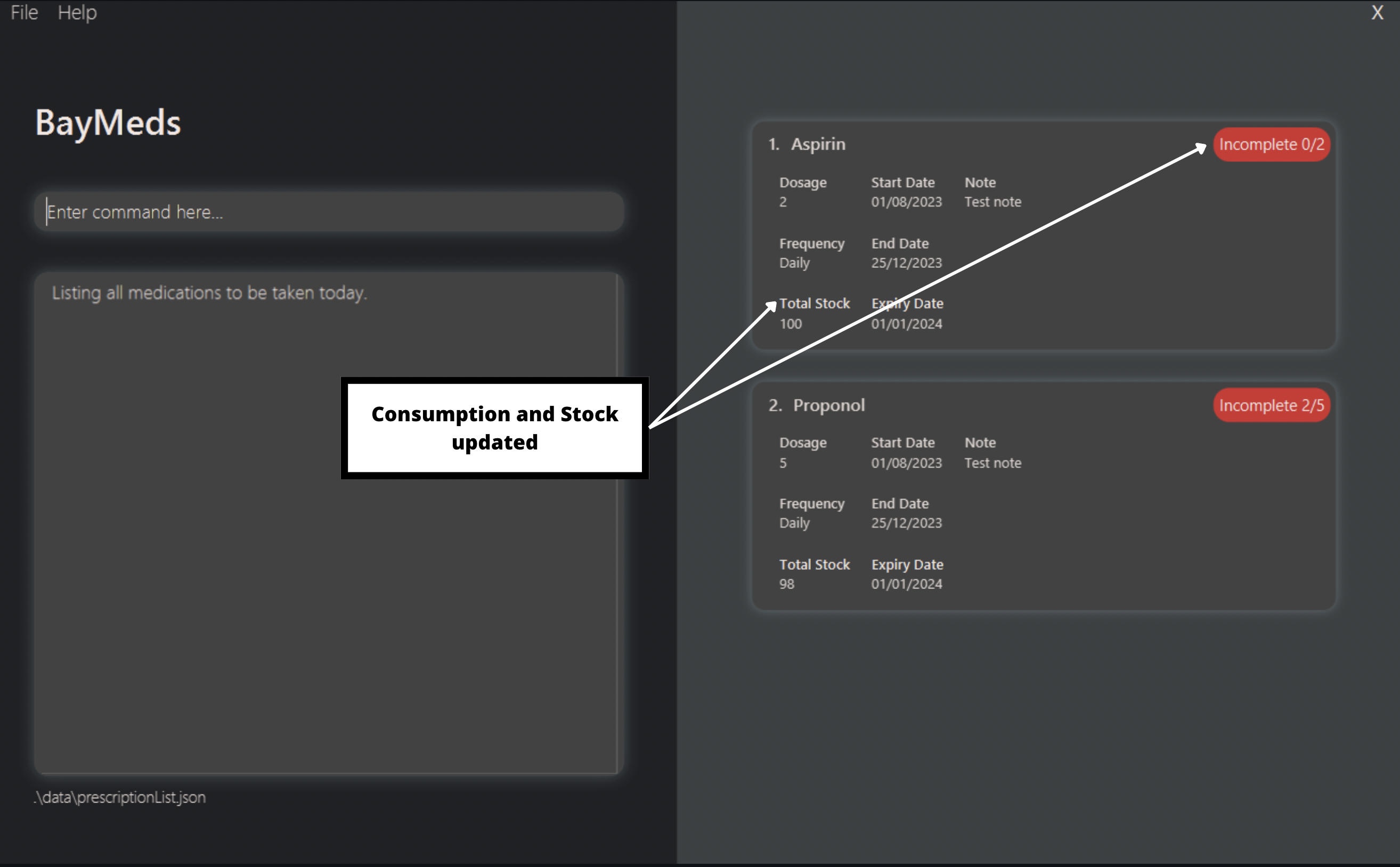
untake 1
By typing this, you will update 1 dose from the first prescription as not consumed.
Using the same prescription list as shown in take, you will get the following result:
As shown in this example, the dosage to untake is set as 1 if not dosage is specified.
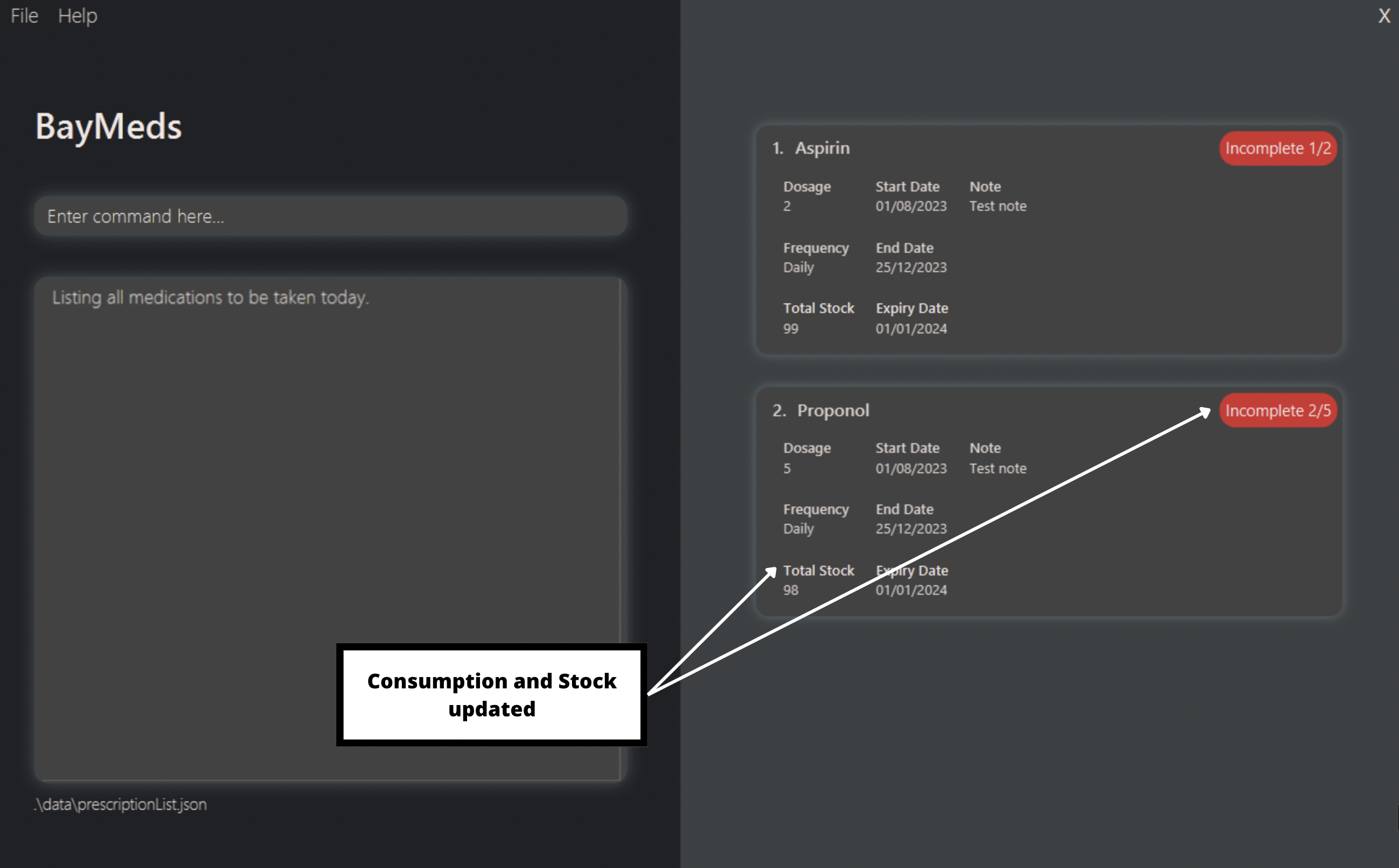
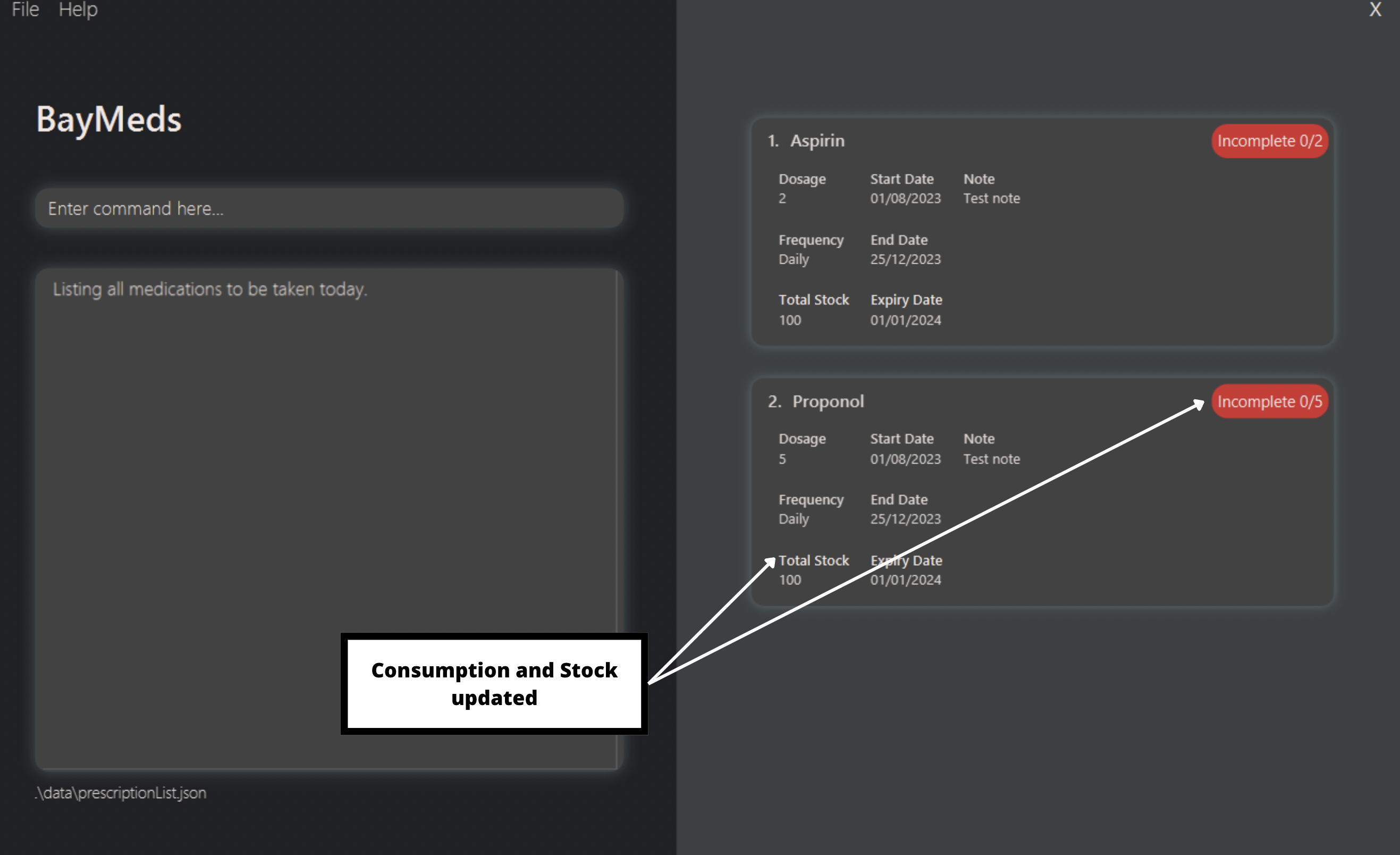
untake 2 d/2
By typing this, you will update 2 doses from the second prescription as not consumed.
Using the same prescription list as shown in take, you will get the following result:
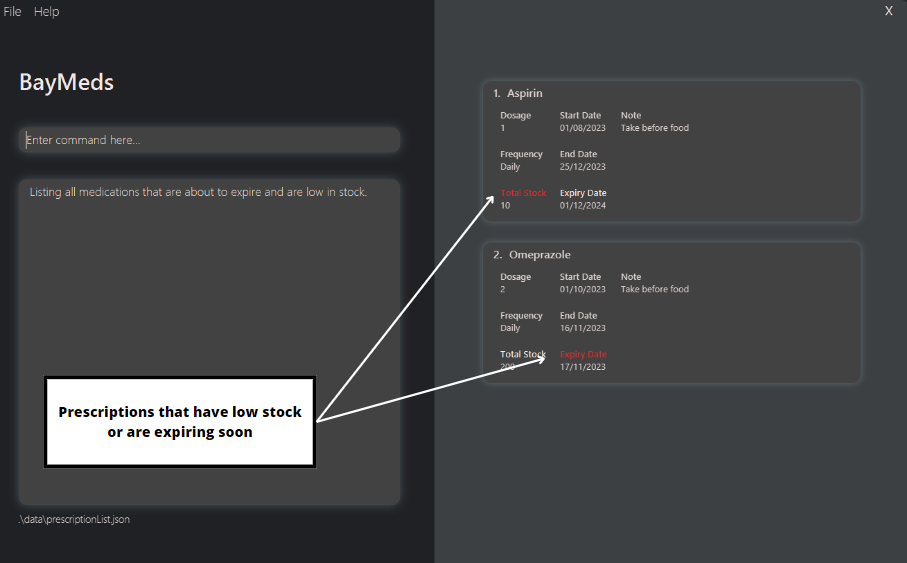
How to list medications that are about to expire or low in stock : reminder
To reduce your risk of running out of medications or consuming expired medications, BayMeds allows you to filter and view prescriptions that are either expiring or low in stock.
To list these prescriptions, type the following command.
Format:
reminder
You will then be able to see the relevant prescriptions.
Notes
Medications that are expiring within the next 7 days will be shown.
Medications that either have less than 10 tabs left or have 7 dosages worth left will be shown.
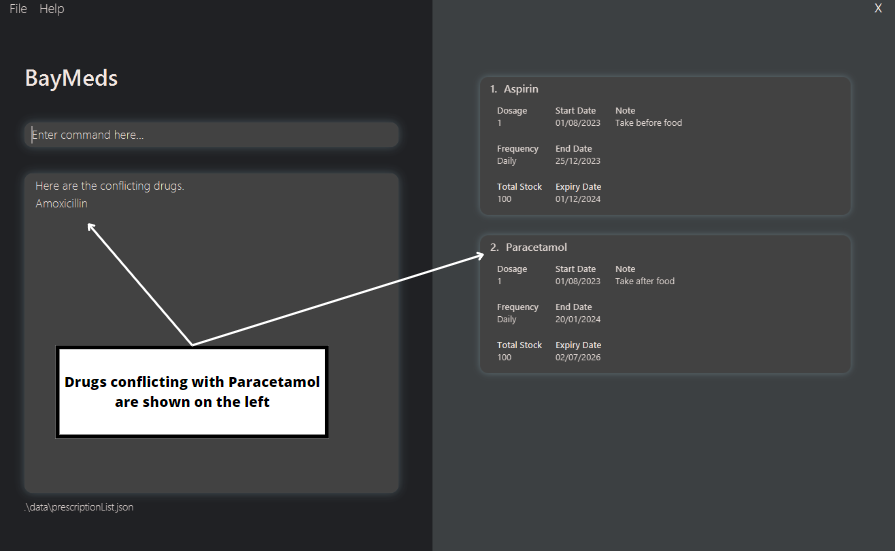
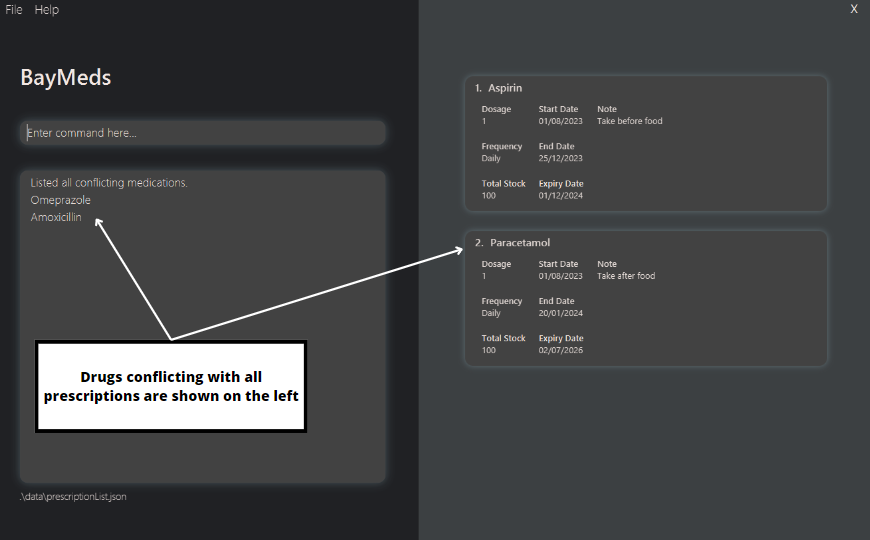
How to list a prescription's conflicting drugs : listConflicts
As you can store drugs that conflict with the prescription, BayMeds allows you to view this list of conflicting drugs.
To view the drugs that conflict with a specific prescription, type the following command.
Format:
listConflicts <index>
You will then be able to see the conflicting drugs in the text box on the left.
Notes
The
<index>specifies the prescription to show.Example
To show the conflicting drugs of the first prescription in the list (currently being displayed), specify the
<index>as 1.This differs from the listAllConflicts command. While
listAllConflictslists drugs that conflict with all your current prescriptions,listConflictswill only list drugs that conflict with the specified prescription.
Important
If the currently displayed list shows your completed prescriptions (i.e. prescriptions that you have consumed in the past), listConflicts will not follow this list. Instead, it will use the list based on the most recently displayed list from either list or listToday.
How to list all conflicting drugs : listAllConflicts
Should you need to see all the drugs that conflict with all your current prescriptions, BayMeds allows you to view all these drugs in a single list.
In order to list all conflicting drugs, type the following command.
Format:
listAllConflicts
You will then be able to see all conflicting drugs in the text box on the left.
Notes
- This differs from the listConflicts command.
listAllConflictslists drugs that conflict with all your current prescriptions, whilelistConflictswill only list drugs that conflict with a specified prescription.
How to view help : help
If you need more information about how to use BayMeds, BayMeds allows you to view our User Guide.
To open the help window, type the following command.
Format:
help
You will then see a help window with the link to our User Guide pop up.
How to exit BayMeds : exit
To exit BayMeds, type the following command.
Format:
exit
FAQ
How do I save my data?
BayMeds data are saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data. There is no need to save manually.
How do I edit the data file?
BayMeds data are saved automatically as a JSON file [JAR file location]/data/prescriptionList.json and completedPrescriptionList.json. Advanced users are welcome to update data directly by editing that data file.
Caution: If your changes are in an invalid format, BayMeds will discard all data and start with an empty data file at the next run. Hence, it is recommended to make a backup of the file before editing it.
How do I store the size and colour of the pill?
You may add it as a note when adding the prescription.
How do I know if I have taken the medication for the day?
Use listToday to list out all medications to be taken for the day.
Medications with a green label will indicate that they have been taken while those with a red label will indicate otherwise.
What should I do if I accidentally add a prescription with an end date to be in the past?
By doing this, the prescription will now be stored as a completed prescription. Thus, it will not be shown in your list of current prescriptions.
What should I do if I accidentally set the end date of a prescription to be in the past?
By doing this, the prescription will now be stored as a completed prescription. As mentioned in listCompleted, interacting with this list is disabled by design. Thus, you may add a new prescription with the same details but corrected end date using the add command.
Is my data shared with other software or organisations?
Data is stored locally in the computer and is not stored in any external database nor shared with other third parties.
We recommend locking your device before leaving it unattended to prevent others from accessing your prescription records and consumption history.
How do I transfer my data to another computer?
Install the app in the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the data of your previous BayMeds home folder.
What if I eat extra medication by accident?
The application allows you to take extra dosages even if it differs from the intended frequency and dosage.
This allows you to correctly and effectively track dosages that you may have mistakenly taken.
Can I manually reset the completion status of a medication?
No, the completion status of a medication is automatically reset upon the beginning of a new day.
If you have wrongly inputted the taking of a medication, use the untake command.
What happens if my drug has no valid details but I take it?
You will still be allowed to take the drug, allowing you to keep track of the drugs that you have taken.
Known issues
- When using multiple screens, if you move the application to a secondary screen, and later switch to using only the primary screen, the GUI will open off-screen. The remedy is to delete the
preferences.jsonfile created by the application before running the application again. - When adding conflicting drugs, if you are handling complex drugs, drugs with names longer than a word (such as "Ascorbic acid") cannot be added as drug names are space separated. We will implement a fix for this in the future.
- When adding conflicting drugs, if you leave the /cfdg field empty or without alphanumeric characters, the error message will be the same as if you left the /mn parameter empty. We will implement a fix for this in the future.
- When adding conflicting drugs, if you add drugs in a different case to the /cfdg field (e.g. ASPIRIN, aspirin, AspIrIN), BayMeds will add each of them as a new conflicting drug. BayMeds will not show a warning if the conflicting drug to be added does not exactly match the case of the existing prescriptions. We will implement a fix for this in the future.
- When taking prescriptions, if you overdose and
takemore than the dosage stored in BayMeds, there will not be an error message to warn you. We will implement a fix for this in the future. - When adding prescriptions, if you name your prescriptions with numbers "1", "234" or "4 5 6", BayMeds will add this prescription as per normal. As these names do not properly identify the exact prescription stored in BayMeds, we will implement a fix for this in the future.
- When taking prescriptions, we will implement a feature that automatically reminds you when it is time to eat your medication.
Glossary
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Medication | A drug identified by a name. |
| Prescription | Uniquely identified by a medication and a start date. |
| Conflicting drugs | Drugs that should not be taken together, e.g. drugs that react with other drugs or affect the efficacy of other drugs |
| Command | One of the commands in the command summary below, each command has a unique format. |
| Parameters | Additional information supplied to a command. Some parameters are compulsory while others are optional, please refer to the command summary below. |
| Index | A number indicating the position of a prescription in the list of prescriptions. The first prescription in the list has an index of 1. |
Command summary
| How to ... | Format, Example |
|---|---|
| Add a prescription | add mn/<medication_name> [d/<dosage>] [f/<frequency>] [sd/<start_date>] [ed/<end_date>] [exd/<expiry_date>] [ts/<total_stock>] [n/<note>] [cfdg/<conflicting_drugs>], e.g. add mn/Aspirin d/1 f/Daily sd/20/09/2023 ed/03/10/2024 exp/04/10/2024 ts/100 n/Take during meals cfdg/Panadol |
| List all prescriptions | list |
| List today's prescriptions | listToday |
| List completed prescriptions | listCompleted |
| Edit prescriptions | edit <index> [mn/<medication_name>] [d/<dosage>] [f/<frequency>] [sd/<start_date>] [ed/<end_date>] [exd/<expiry_date>] [ts/<total_stock>] [n/<note>] [cfdg/<conflicting_drugs>], e.g. edit 1 mn/Aspirin d/1 f/Daily sd/20/09/2023 ed/03/10/2024 exp/04/10/2024 ts/100 n/Take during meals cfdg/Panadol |
| Find prescriptions | find <keyword>, e.g. find Aspirin |
| Delete prescriptions | delete <index>, e.g. delete 2 |
| Take prescriptions | take <index> [d/<dosage>], e.g. take 1 d/1 |
| Untake prescriptions | untake <index> [d/<dosage>], e.g. untake 1 d/1 |
| View expiring/low in stock prescriptions | reminder |
| List conflicting prescriptions | listConflicts <index>, e.g. listConflicts 1 |
| List all conflicting prescriptions | listAllConflicts |
| Show help | help |
| Exit the application | exit |
Troubleshooting
Noticed some error messages? You may refer to this section to find out some possible causes.
This prescription already exists in the prescription list.
You attempted to add a prescription with identical details to one already present in the list.
You attempted to edit a prescription such that it has identical details to one already present in the list.
There are conflicting drugs in BayMeds.
You added a prescription that conflicts with other drugs in the list.
This is simply a warning and can be ignored.
Start date cannot be after end date and expiry date cannot be before start or end date.
You attempted to add a prescription with incorrect dates.
You attempted to edit a prescription such that it has incorrect dates.
The prescription index provided is invalid.
You attempted to execute a command on an index that does not exist in the list.
At least one field to edit must be provided.
You attempted to edit a prescription without providing any fields to be edited.
No prescriptions found.
You attempted to list some prescriptions, but none matching your query were found.
No medications to be taken today.
You attempted to list out medications to be taken today, but none were found.
No reminders.
You attempted to list out medications that are about to expire or low in stock, but none were found.
The specified prescription does not exist.
You attempted to execute a command on a prescription that does not exist in the list.
There is insufficient stock for this prescription.
You attempted to take a medication but there is not enough stock to deduct from for the amount you entered.
Cannot untake more than what you have consumed.
You attempted to untake a medication but the consumption count is already 0.